Our bottom line: Dashlane has an edge with plan variety, robust features, and security, which are important priorities when choosing a password manager.
Dashlane vs. LastPass Overview
Dashlane and LastPass ranked highly among the best password managers. These services are comparable in price, features, security, and compatibility. Both are simple to use, and I had an easy time navigating their dashboards.
Dashlane comes out ahead because of its robust features like a virtual private network (VPN) for Premium users and Team or Business subscribers. Both offer a free plan for one device only, but you’ll find more plan variety with Dashlane, along with no record of security breaches so far.
Which password manager should you get? Let this Dashlane vs. LastPass face-off help you decide.
| Review factor | Winner |
|---|---|
| Price | Dashlane (4.7) |
| Platform compatibility | Tie: Dashlane (5.0), LastPass (5.0) |
| User experience (UX) | LastPass (5.0) |
| Form filling | Dashlane (4.7) |
| Security | Dashlane (4.7) |
| Two-factor authentication (2FA) | LastPass (4.7) |
| Best overall | Dashlane (4.7) |
Dashlane vs. LastPass: Specs
| Password manager | Details | Basic plan features |
| Dashlane Overall rating: 4.75/5 Read our full Dashlane review. | Starting price: Free Platform compatibility: Android, iOS, Linux, Mac, Web (Brave, Chrome, Edge, Firefox, Opera, Safari), Windows Security: AES 256-bit encryption, 2FA |
|
| LastPass Overall rating: 4.4/5 Read our full LastPass review. | Starting price: Free Platform compatibility: Android, iOS, Mac, Web (Chrome, Firefox, Opera, Safari, Edge), Windows, Linux Security: AES 256-bit encryption, 2FA |
|
Dashlane vs. LastPass: Plans and Pricing
Price winner: Dashlane | |
|---|---|
| Dashlane (5/5) | $0 for Free and one device; $2.75 per month for Advanced; $4.99 per month for Premium; $7.49 per month if you pay annually (20% discount). Business plans include Starter for up to 10 seats, billed monthly at $2 per seat; Team for $5 per month, billed annually for unlimited seats; and Business for $8 per seat billed annually. |
| LastPass (4.5/5) | $0 per month for Free; $3 per month for Premium (one user); $4 per month for Family and up to six users; $4 per month per user for Team and up to 50 people; $6 per month per user for Business enterprise level |
While Dashlane costs more for upper-tier plans, the features you get make the password manager a better value, in my opinion. For example, the Premium plan for individuals that allows multiple devices also includes a VPN to protect your Wi-Fi.
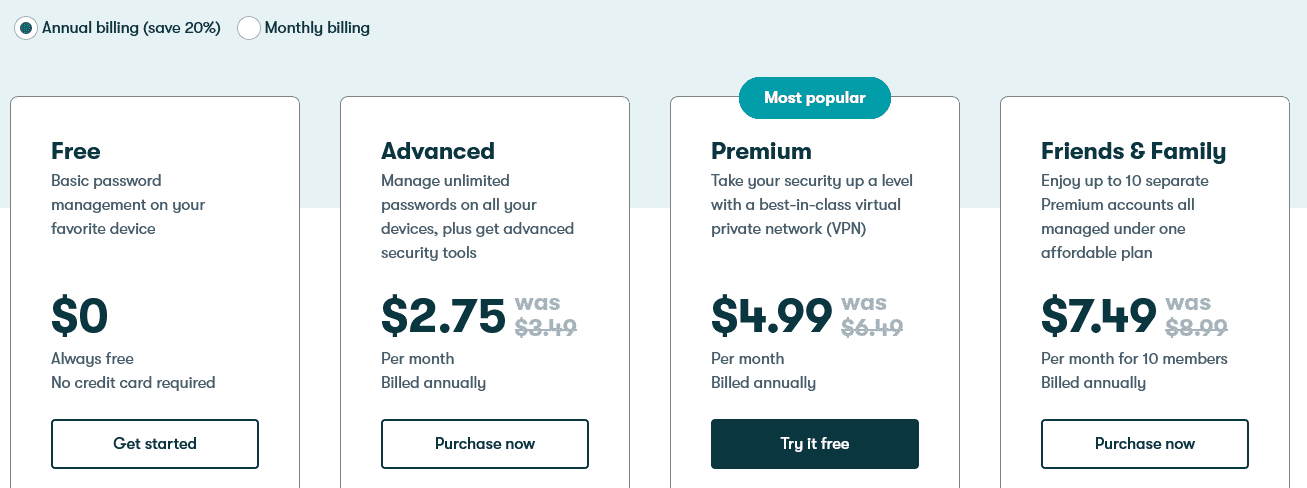
While the Premium plan costs less with LastPass, it doesn’t include a VPN, and I accessed better features from Dashlane Advanced, which is slightly less than LastPass’s individual plan. That said, you get dark web monitoring with DashPass’s free version and must upgrade if you want this feature from Dashlane.
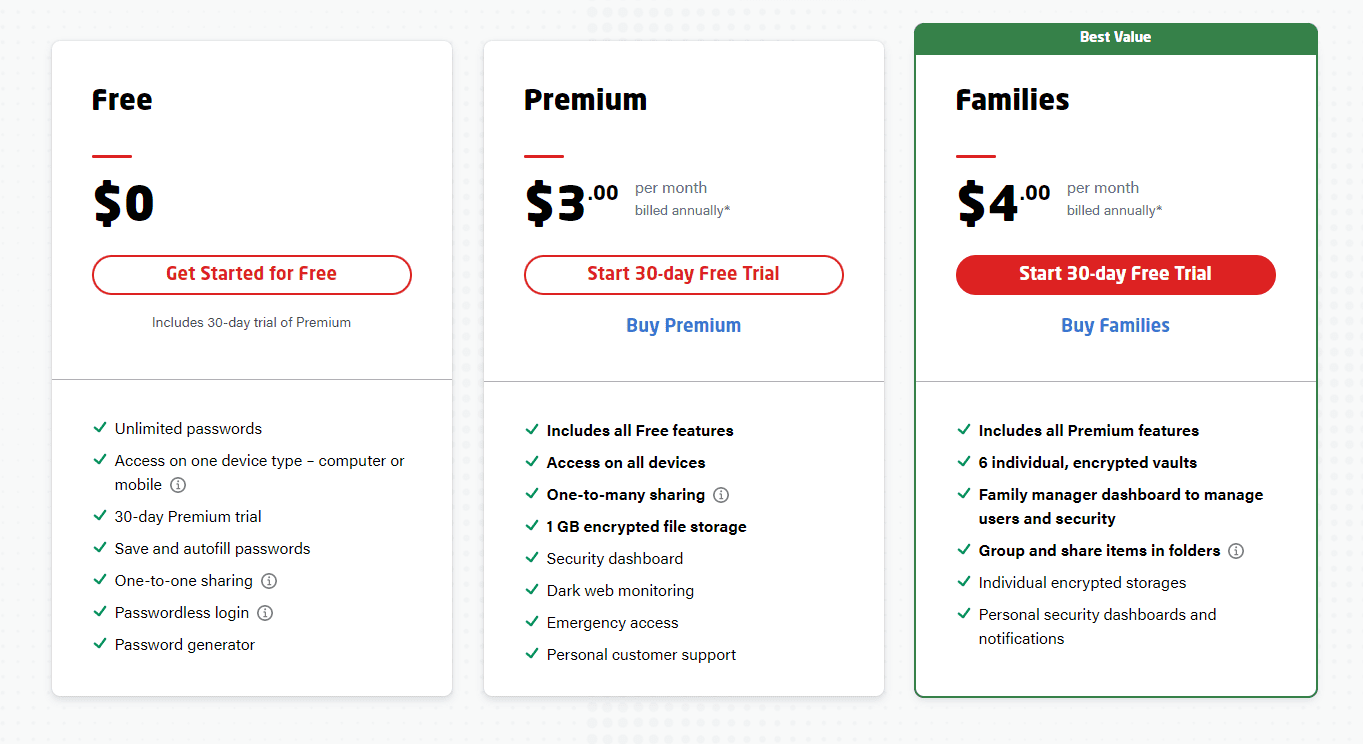
I think LastPass has a real edge with its free tier. Unfortunately, I find it isn’t the deal it used to be, as the plan is now limited to syncing data only among computers or only among mobile devices.
Overall, you’ll find more plan variety with Dashlane and robust features that LastPass does not offer — such as a VPN.
Winner: Dashlane wins plans and pricing because it offers more plan variety and a VPN for Premium at just $4.99 per month.
Dashlane vs. LastPass: Platform Compatibility
Platform compatibility winner: Tie | |
|---|---|
| Dashlane (5/5) | OS: Android (Oreo or later), iOS (15 or later), Linux (latest distributions), Mac (Monterey 12.0 or later), and Windows Supported browsers: Brave, Chrome, Edge, Firefox, Opera, Safari |
| LastPass (5/5) | OS: Windows (version 8.1 and up), Chrome OS, Linux, Android, MacOS, Linux Supported browsers: Chrome, Edge, Firefox, Opera, Safari |
LastPass and Dashlane are compatible with similar operating systems and browsers, and Dashlane stands out for its ability to be added to devices like Kindles through the Google Play store.
LastPass recommends running Windows 8.1 and above, Catalina 10.15 (for macOS), Chrome OS, or one of the most common distributions of Linux. Supported browsers include Chrome, Edge, Firefox, Safari, and Opera.

There are two types of LastPass browser extensions; you can find the first in your browser’s extensions library. (Brave and Vivaldi can use this Chrome extension, and SeaMonkey the Firefox one.) On mobile, LastPass is available for iOS 13 and up.
Full support with automatic form-filling requires Android 8.0 Oreo or later. Still, the app will run on Android 5.0 Lollipop and later.

Dashlane vs. LastPass: UX
UX winner: LastPass | |
|---|---|
| Dashlane (4.75/5) | Simple interface is user-friendly |
| LastPass (5/5) | Minimal – in a good way |
Dashlane and LastPass are intuitive and easy to learn. I had no problem finding my way around either of the password managers’ dashboards. They also both have simple interfaces that are seamless to navigate.
Yet Dashlane’s browser extension was a bit cluttered because it’s a condensed version of the desktop. The good part about that is consistency. But it could be more streamlined. (This is getting picky.)
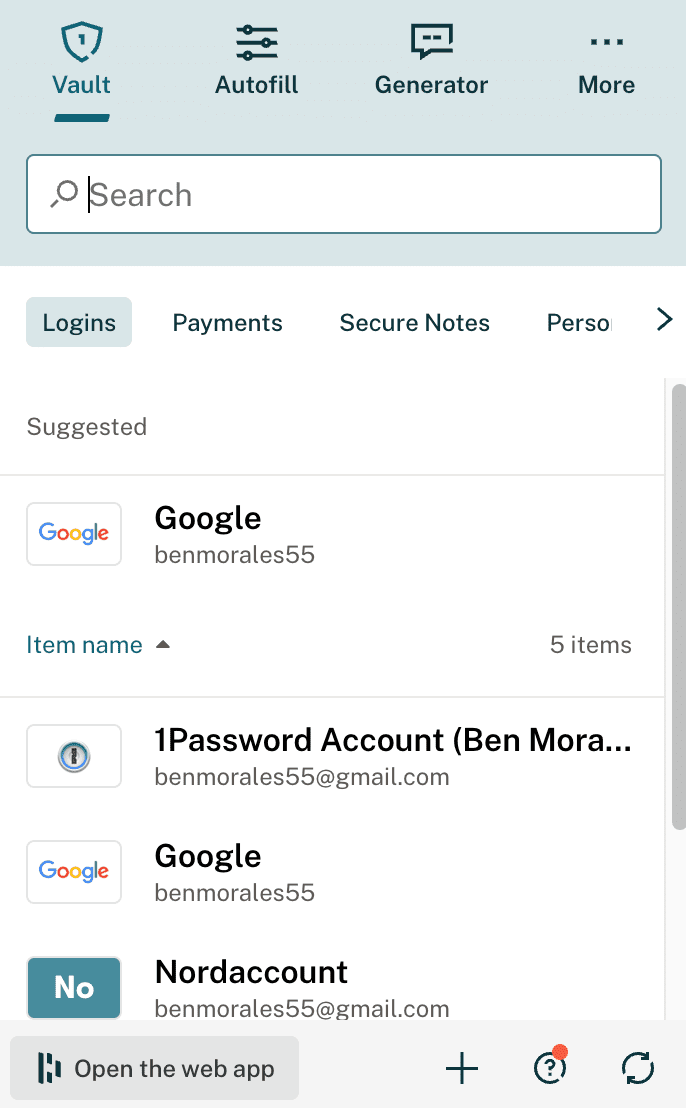
The LastPass desktop app has six primary and five secondary sections, making it a bit more like the web experience. While the macOS version is fairly robust, the Windows desktop app is no longer being developed and has some significant limitations.

What I love about LastPass is its user incentive program that supports you for exploring its features. You receive a 10% discount for completing “achievements” that teach you how to use the platform. As you explore the service, you can also save money on the annual subscription. Plus, this incentive encouraged me to dig into the service and really use its features.
Importing passwords from other stand-alone and browser-based password managers is a breeze in LastPass, which supports imports from nearly 30 platforms. With Dashlane, you have to export passwords to a CSV file. I felt this process was simple, though you can’t import a CSV file to Dashlane using the iOS or Safari app. You must use Dashlane’s web app or Android app.
Winner: LastPass wins UX because of its creative incentive program, clean browser extension, and ease of importing passwords from other password managers.
Dashlane vs. LastPass: Form Filling
Form filling winner: Dashlane | |
|---|---|
| Dashlane (4.75/5) | macOS: Mobile browsers and apps ( iOS 15 or later) Android: Mobile browsers and apps (Android Oreo or later) |
| LastPass (4.5/5) | macOS: Chrome, Edge, Safari, Opera, Firefox Android: Chrome, Edge, Safari, Opera, Firefox |
Both Dashlane and LastPass offer robust form-filling — including logins, addresses, and credit card information — on both desktop and mobile.
LastPass’s form-filling function on mobile devices works via a Safari browser extension for iOS 8 and above and as a built-in app feature for Android 8.0 Oreo or later.
With LastPass, the red box in the corner of any form it detects alerted me to click the button and select my information from a drop-down menu. You can choose a certain profile if multiple users share the account, and the form fills out automatically.
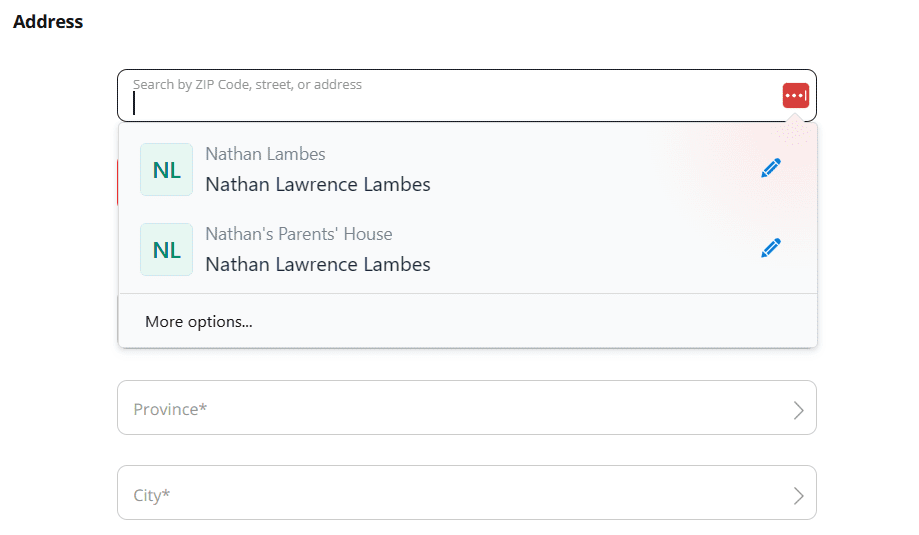
To autofill forms in Dashlane, I only had to place the cursor in the field. A list of information popped up so I could make a selection. For example, if I was filling in an email field, I selected the correct login, and Dashlane took care of the rest.
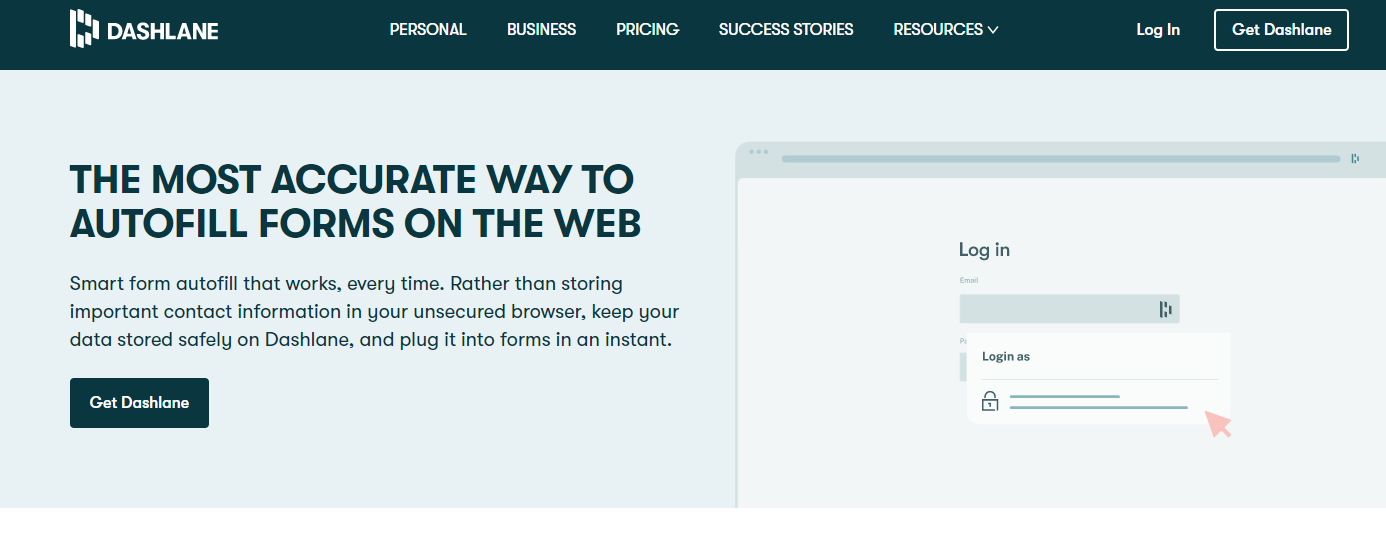
Overall, I found Dashlane’s built-in sections for logins, payment information, addresses, and IDs easy to input and autofill.
Winner: Dashlane has a slight edge in form-filling with built-in fields that suit most users’ needs.
Dashlane vs. LastPass: Security
Security winner: Dashlane | |
|---|---|
| Dashlane (4.75/5) |
|
| LastPass (3/5) |
|
Most password managers, including LastPass and Dashlane, use powerful 256-bit AES encryption, and both password managers’ vaults are unlocked on your device only after you’ve entered your master password.
If you are a paid LastPass user, you can gain access to the Security Dashboard that analyzes all your stored passwords for weaknesses and whether any have been compromised in data breaches. Dashlane also offers password health, and both have zero-knowledge architecture.
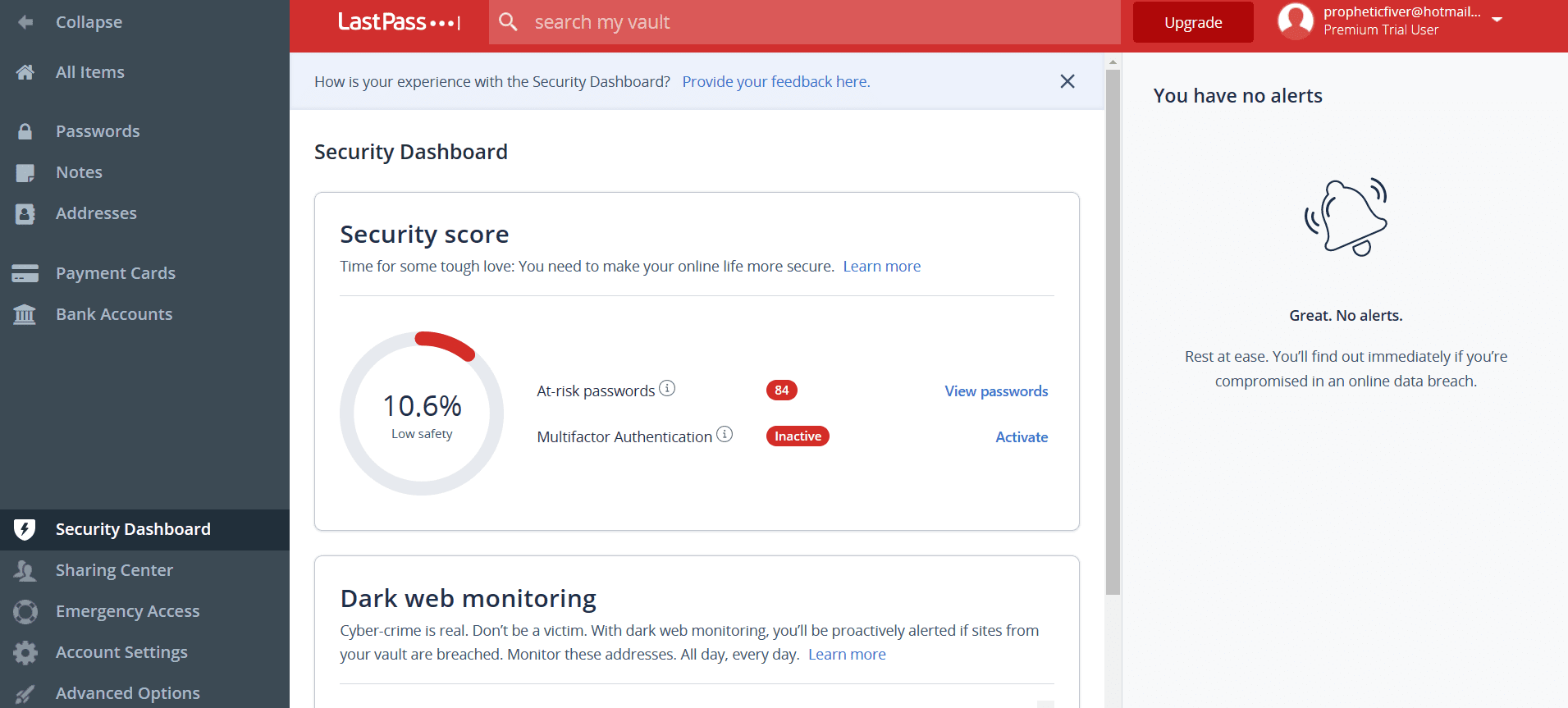
I like how Dashlane offers live dark web monitoring and a VPN if you select its Premier individual plan, or Teams and Business tiers. You can also choose to add on Dashlane’s licensed version of Hotspot Shield, which costs $12.99 per month on its own. If I elected this option as a Dashlane subscriber, I’d only have to pay $4.99 per month.
Both platforms are Service Organization Controls (SOC 2) compliant, meaning they have carefully documented security policies and undergo regular audits. (Here are our tips on protecting your online passwords.)
But the downside to LastPass is that it experienced two security breaches last year, whereas there is no record of security breaches for Dashlane. LastPass is transparent about the incidents. It provided this security breach statement that states the company completed a thorough investigation and has not identified any threat-actor activity since Oct. 26, 2022.
LastPass says it has invested resources to improve overall security operations. The company shared that the threat did not originate in-house but from third parties. While I wouldn’t discount LastPass’s secure environment because of these incidents, the winner is clear if we compare LastPass to Dashlane with no security breaches.
Winner: Dashlane wins security because it has not experienced a breach.
Dashlane vs. LastPass: 2FA
2FA winner: LastPass | |
|---|---|
| Dashlane (4.25/5) |
|
| LastPass (4.75/5) |
|
Both LastPass and Dashlane support 2FA via authenticator apps (which use time-based one-time passwords, or TOTPs) and physical security keys.
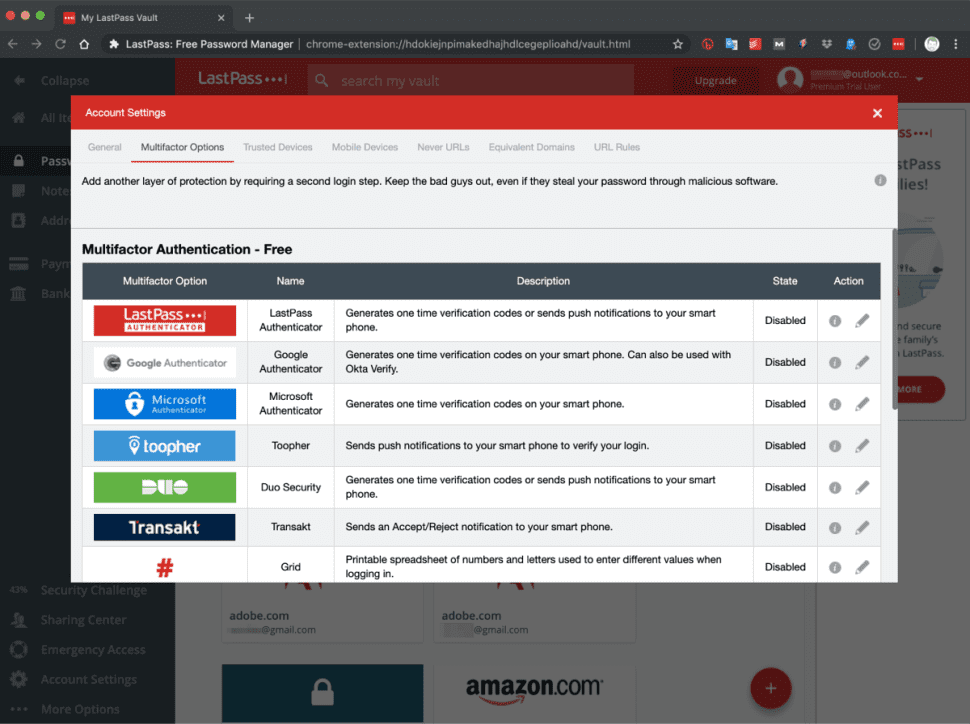
LastPass’s free plan works with authenticator apps, including LastPass Authenticator, Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator, Duo Security, and Transakt. Those with a premium subscription can also use hardware authenticators such as Yubico’s YubiKey, a fingerprint sensor or a smart-card reader. The platform also offers an MFA feature called Grid, a chart you can print out to generate security codes manually.
Dashlane’s 2FA is optional, and there is currently no biometric option, which would be preferred. You can enable MFA through the Dashlane authenticator. I added a layer of security to specific log-ins by selecting those in the Logins section of Dashlane’s web app. Then in Preferences, all you have to do is turn on Require Master Password.
Winner: LastPass wins 2FA because of available fingerprint sensors for premium plans.
Should You Get Dashlane or LastPass?
Bottom line winner: Dashlane | |
|---|---|
| Dashlane (4.75/5) |
Best for: Individuals or businesses that want premium features like a VPN and dark web monitoring |
| LastPass (4.4/5) |
Best for: Flexibility with no time limit on the free plan, rewards to save on cost, and ease of use |
Dashlane comes out ahead with more plan variety, features like a VPN, and tight security with no record of security breaches as of publication. Both are considered among the best password managers and tie for platform capability.
LastPass has a leg up when it comes to importing passwords from other platforms, and it also has a slight edge with 2FA because of the ability to get fingerprint sensors if you select a premium plan.
Both password managers use the gold standard 256-bit AES encryption. But LastPass is dealing with the fallout of a few security breaches that it has addressed by hardening security across the board. That said, Dashlane has a clean record, so that gives me a bit more peace of mind.
Overall, Dashlane and LastPass offer competitive, comprehensive password manager services. I chose Dashlane because of the robust features and security.
How I Evaluated Dashlane vs. LastPass
On the surface, all password managers essentially generate and store passwords. As I evaluated providers, I dug deeper, comparing software on what matters most, including price, platform compatibility, security, and other factors.
I signed up for a plan with each provider to test:
- Plan value: Most password managers offer various subscription plans from free to around $20 per month. While free plans may be sufficient for some, those that need more functionality may prefer paid plans. We included a wide array of free and paid password managers to find the one that works best for you.
- Platform compatibility: You likely access your online accounts from multiple devices, including desktops, laptops, tablets, phones, as well as through different web browsers. Your password manager should be compatible with various devices, operating systems and browsers, and sync seamlessly between them all.
- UX: This is how you interface with all the features and functions of your new password manager — if it’s bad, you’ll be less likely to use the service. While this is a highly subjective category and some will disagree, it’s important to provide an overview based on my experience.
- Form filling: A password manager doesn’t have to include form-filling, but it’s somewhat standard and the ease with which it performs that function can be the deciding factor in which password manager you ultimately choose.
- Security: Since a password manager is first and foremost a security tool, it should come with all of the most up-to-date standard security features. This includes the highest level of available encryption (256-bit AES with PBKDF2-HMAC-SHA512); 2FA, such as biometric logins or MFA, and a password generator.
- Two-factor authentication (2FA): Used all over the internet to protect your accounts, this is quickly becoming a standard security practice. 2FA is a great way to secure more sensitive accounts to ensure they’re not breached.
Learn more about our review methodology.

About the Password Manager, Gunnar Kallstrom:
Kallstrom is a Cyber Team Lead for a Department of Defense (DOD) contracting company in Huntsville, Alabama, and has also worked as a computer network defense (CND) Cyber Analyst. An author and content creator for a cybersecurity academy, Kallstrom spent nearly 15 years in the Army as a musician before entering the cybersecurity field.
He holds a bachelor’s degree in music from Thomas Edison State University and a master’s in organizational development and leadership from the University of the Incarnate Word.
Kallstrom has completed several Computing Technology Industry Association (CompTIA) courses, including Security+, Network+, A+ Core 1, and A+ Core 2. He earned a CompTIA Security+ Certification. Additionally, he has completed the Cyber Warrior Academy program with more than 800 hours of hands-on, intensive, and lab-driven technical training in cybersecurity methods and procedures.
Passionate about all things cyber, Kallstrom was a speaker on a panel at the 2022 InfoSec World conference, giving a talk entitled “Hacking into a Cyber Career – True Stories.” Kallstrom is also a mentor to entry-level cybersecurity candidates seeking to break into the field. When he’s not working, he still enjoys playing guitar and fishing (not phishing).



